Introduction
WARP Charger Smart Pro can report their current state and be controlled via MQTT and HTTP. While the MQTT API must first be activated and configured, the HTTP API can be used immediately as it is also used by the web interface itself.
MQTT
If the charger is used with ioBroker, a different MQTT broker than the one available as an ioBroker addon should be used. The ioBroker MQTT broker does not conform to the MQTT specification in several respects, which leads to various problems.
Configuration
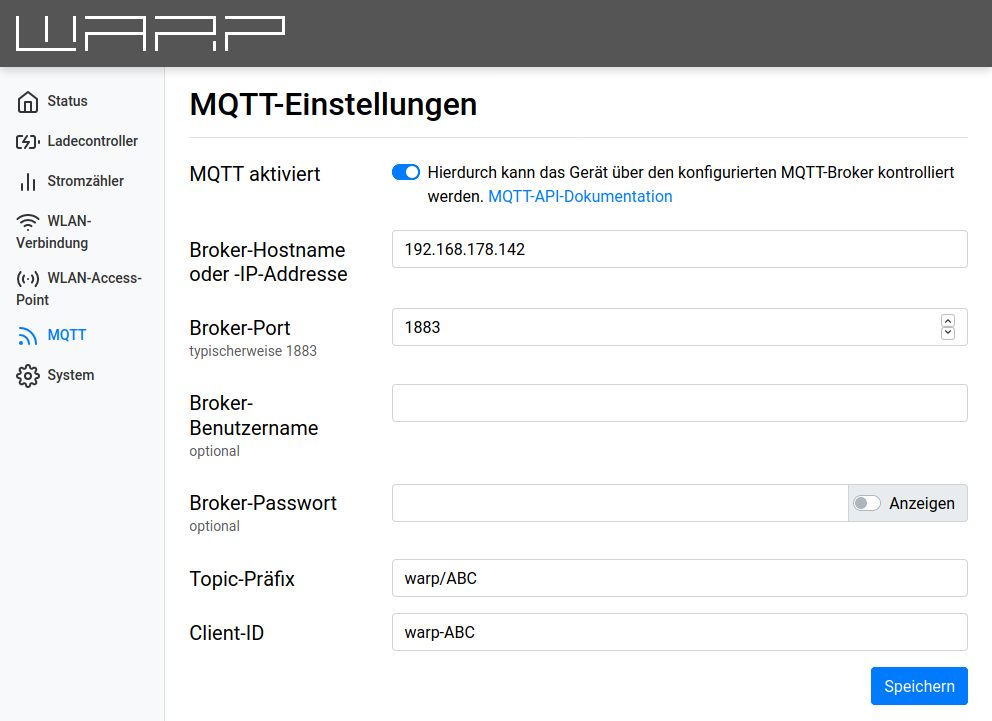
For the charger to communicate via MQTT, the connection to the MQTT broker must first be configured in the web interface. The following settings can be configured:
- Broker hostname or IP address The hostname or IP address of the broker to which the charger should connect.
- Broker port The port under which the broker is reachable. The typical MQTT port 1883 is preset.
- Broker username and password Some brokers support authentication with username and password.
- Topic prefix This prefix is prepended to all topics used by the charger. The default is
warp/AbCd,warp2/AbCd,warp3/AbCdorwem/AbCdwhereAbCdis a unique identifier per charger, but other prefixes such as garage_left are possible. If multiple chargers communicate with the same broker, unique prefixes must be chosen per box. - Client ID The charger registers with the broker using this ID.
After the configuration is set and the "MQTT enabled" switch is set, the configuration can be saved. The ESP then restarts and connects to the broker. The status page shows whether the connection could be established.
In the following, the mosquitto_pub and mosquitto_sub commands of the Mosquitto MQTT broker are used to communicate with the broker.
Basics
Once the connection to the broker has been successfully established, the first messages from the charger should now arrive. All messages from the charger are strings in JSON format. Likewise, all messages sent to the charger must comply with the JSON format.
With
mosquitto_sub -v -t "warp/AbCd/#"
all messages from the charger can be displayed. (Replace the prefix warp/AbCd with the configured one) For example, the following message could be received on warp/AbCd/evse/state:
{
"iec61851_state": 1,
"charger_state": 2,
"contactor_state": 1,
"contactor_error": 0,
"allowed_charging_current": 32000,
"error_state": 0,
"lock_state": 0,
"dc_fault_current_state": 0
}
The messages of the topic evse/state provide an overview of the charge controller's state. For example, the allowed charging current is currently 32000, i.e. 32 amperes.
By sending the message {"current":8000} to the topic evse/global_current_update, the charging current can be limited to 8 amperes, for example like this:
mosquitto_pub -t "warp/AbCd/evse/global_current_update" -m "{\"current\": 8000}"
(To make the examples compatible with cmd.exe on Windows, only double quotes are used. Quotes in JSON messages must therefore be escaped with .)
For simplification, evse/global_current_update is used here. The current set with this API is stored in the flash memory of the charge controller and should therefore not be set frequently to preserve the flash memory. Frequent changes to the charging current (e.g. for external control, PV excess charging, etc.) should instead be made via the API evse/external_current_update, which can be activated on the Charger -> Settings page with the "External control" option.
The charging current is now limited to 8 amperes, which the charger indicates with a new message:
{
"iec61851_state": 1,
"charger_state": 2,
"contactor_state": 1,
"contactor_error": 0,
"allowed_charging_current": 8000,
"error_state": 0,
"lock_state": 0,
"dc_fault_current_state": 0
}
APIs that consist of a JSON object with exactly one value can be abbreviated by sending the value directly:
mosquitto_pub -t "warp/AbCd/evse/global_current_update" -m 8000
HTTP
Configuration
The HTTP API can be used without prior configuration. Optionally, access credentials for the web interface and HTTP API can be configured on the Users page (for chargers) or the Credentials page (for the WARP Energy Manager). All requests must then be authenticated with Digest access authentication. Unauthenticated requests are answered by the charger with HTTP code 401. An exception is the main page of the web interface, which responds to most browsers with the login page on an unauthenticated request.
Basics
The HTTP API is structurally identical to the MQTT API: If the MQTT API uses the topic warp/AbCd/evse/state, for example, the same API can be accessed via the URL http://warp-AbCd/evse/state. However, the HTTP API has some advanced features that are not available via MQTT. Additionally, WebSockets can be used at, for example, ws://warp-AbCd/ws. Via a WebSocket connection, the charger (analogous to MQTT) automatically transmits updated values.
To receive all messages sent by the charger analogous to the MQTT example, a WebSocket connection can be used. For this and for the further examples, websocat and curl are used and it is assumed that the charger is reachable under the hostname warp-AbCd.
With websocat ws://warp-AbCd/ws, among other things, the following message could be received:
{
"topic": "evse/state",
"payload": {
"iec61851_state": 1,
"charger_state": 2,
"contactor_state": 1,
"contactor_error": 0,
"allowed_charging_current": 32000,
"error_state": 0,
"lock_state": 0,
"dc_fault_current_state": 0
}
}
This message is equivalent to the one from the MQTT basics, but the MQTT topic is here part of the JSON structure, as no comparable concept exists for WebSockets.
If only one piece of information needs to be queried, a single URL can be called with curl:
curl -s http://warp-AbCd/evse/state
delivers equivalent JSON data:
{
"iec61851_state": 1,
"charger_state": 2,
"contactor_state": 1,
"contactor_error": 0,
"allowed_charging_current": 32000,
"error_state": 0,
"lock_state": 0,
"dc_fault_current_state": 0
}
With jq, individual values can be extracted from a JSON object:
curl -s http://warp-AbCd/evse/state | jq ".allowed_charging_current"
returns 32000, i.e. the allowed charging current of 32 amperes.
Now the charging current should be limited to 8 amperes. For this, the message {"current":8000} is sent to the URL http://warp-AbCd/evse/global_current_update:
curl -X PUT -d "{\"current\":8000}" warp-AbCd/evse/global_current_update
For simplification, evse/global_current_update is used here. The current set with this API is stored in the flash memory of the charge controller and should therefore not be set frequently to preserve the flash memory. Frequent changes to the charging current (e.g. for external control, PV excess charging, etc.) should instead be made via the API evse/external_current_update, which can be activated on the Charger -> Settings page with the "External control" option.
The following simplifications are possible:
- The example uses the HTTP method
PUT, butPOSTis also accepted. curl automatically usesPOSTwhen data is to be sent. - APIs that can be read on the address
warp-AbCd/Xand written towarp-AbCd/X_updatecan (only via HTTP!) also be written towarp-AbCd/X. - APIs that consist of a JSON object with exactly one value can be abbreviated by sending the value directly.
Combined, setting the charging current can be abbreviated as follows:
curl -d 8000 warp-AbCd/evse/global_current
Now
curl -s http://warp-AbCd/evse/state | jq ".allowed_charging_current"
should return 8000, i.e. 8 amperes.
Unions
Various APIs of the WARP Charger use Unions (also known as Sum types) to express variable objects. A union consists of its data and a tag that indicates which variant of the data is used. A number is always used as the tag. Tag and data are represented in a JSON array with always exactly two entries. A value that should be either an object with two entries or a string could be expressed like this:
[0, {"entry_a": 123, "entry_b": "abc"}]
or
[1, "Hello World"]
A more concrete example: The API meters/1/config configures the energy meter in slot 1. A charger in its default state has only one energy meter configured on slot 0 (the possibly internally integrated meter). Therefore, meters/1/config has the default value
[0, null]
i.e. tag 0 with no additional data (expressed by null)
According to the documentation of this API, tag 0 means that no energy meter is configured.
If instead a meter should be configured that receives its values via the SMA Speedwire protocol (tag 7), the display name of the meter is additionally required. The following configuration must therefore be set:
[7, { "display_name": "My Meter" }]
To determine the content of a specific variant of a union, the tag can be changed without setting new data. For example, if the following configuration is set:
[6, null]
and meters/1/config is then read, the following value is returned:
[6, { "display_name": "", "host": "", "port": 502, "table": [0, null] }]
Tag 6 is a Modbus TCP meter for which the display name, host and port as well as the register table to be used must be specified. The register table is in turn a union.