Introduction
This description refers to the WARP Energy Manager 2.0. For information about the older model (WARP Energy Manager 1.0), please refer to the operating manual at https://warp-charger.com/downloads.
With the WARP Energy Manager, we offer our energy manager for control cabinet mounting, with which energy consumption at home can be monitored, controlled and optimized.

The WARP Energy Manager can control heat pumps via the SG-Ready interface depending on dynamic electricity prices, photovoltaic excess or current load at the grid connection, switch additional consumers on or off, and charge electric vehicles in conjunction with WARP Charger chargers. Control of battery storage charging and discharging processes will also be possible in the future.
Features
The WARP Energy Manager has the following features:
- Integrated local energy monitoring (data storage on the device)
- Control of heat pumps via SG-Ready interface
- Four inputs for potential-free contacts, e.g.: §14a EnWG - Controllable Consumption Device
- Two relay outputs for controlling additional consumers
- Control of up to 64 WARP Charger chargers
- Control of battery storage (future)
- Access to electricity meters at grid connection, photovoltaic inverters, battery storage
- Photovoltaic excess utilization
- Static and dynamic load management of WARP Chargers
- Photovoltaic forecast
- Dynamic electricity prices
Integrated Energy Monitoring
The WARP Energy Manager displays the measured values of the electricity meters in its web interface. It shows how much power is drawn from the grid or fed in (if a photovoltaic system is present). Additionally, other data can be displayed, for example from PV inverters and battery storage, or the dynamic electricity price. Power and other measured values are displayed live on the web interface.
Every five minutes, the measured values are saved locally on the energy manager's microSD card. This makes the WARP Energy Manager independent of data recording on cloud servers. You can view this data graphically for each day. This allows you to analyze your energy consumption on a daily, monthly and annual basis.
Control of Chargers
The WARP Energy Manager can control up to 64 chargers of type WARP Charger Smart or WARP Charger Pro depending on consumption. Control is via a common network (LAN, WiFi) between the chargers and the WARP Energy Manager. Static load management can be performed, where a fixed current is divided among the chargers according to demand. Alternatively, dynamic load management can also be set up. The current at the grid connection is measured by an electricity meter. The WARP Energy Manager then regulates the chargers so that the set maximum current at the grid connection is not exceeded. With various settings, you can define under which conditions and with how much power vehicles are charged.
SG-Ready Interface for Controlling Heat Pumps
The WARP Energy Manager has an SG-Ready interface with which heat pumps can be controlled. According to the standard, this consists of two relay outputs. One output can completely block the heat pump, for example when the electricity price exceeds a threshold. The second output can put the heat pump into extended operation mode, in which the heating circuit and hot water temperatures are slightly increased. This allows efficient use of photovoltaic excess or cheap electricity prices. If neither output is switched, the heat pump operates normally.
Two Relay Outputs for Controlling Additional Consumers
The WARP Energy Manager has two relay outputs. With these outputs, for example, 230V consumers can be switched directly or larger loads via an intermediate contactor. As an example, heating elements can be controlled this way.
Four Inputs, e.g. for §14a EnWG - Controllable Consumption Device
A potential-free contact (normally open/normally closed) can be connected to each of the four inputs of the WARP Energy Manager. These inputs can be used for user-configurable rules. One application is using an input to reduce the power of chargers and heat pumps controlled by the Energy Manager according to §14a EnWG.
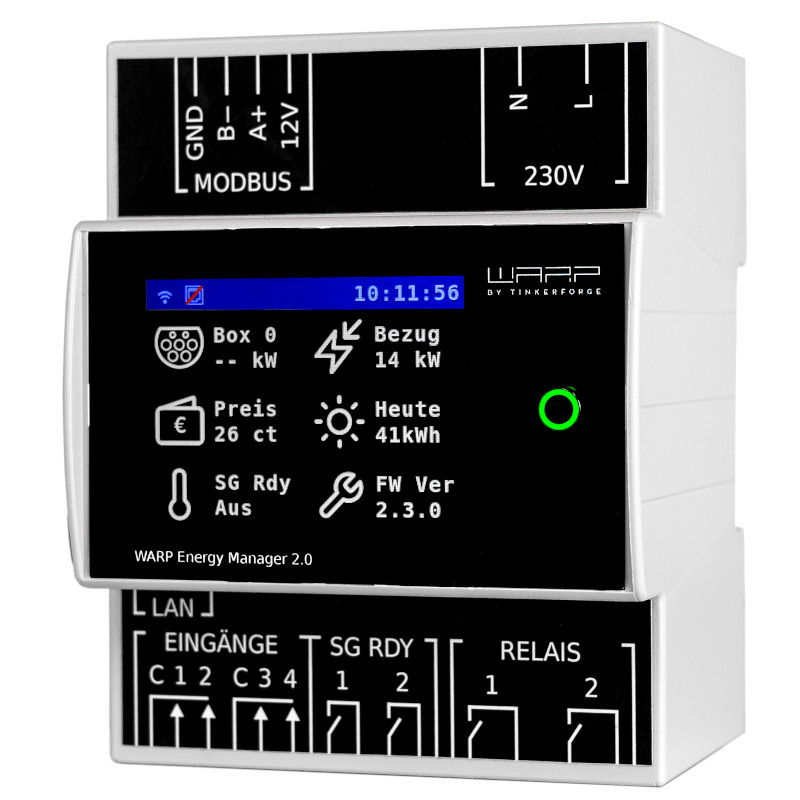
Front Button with Display
A 320x240 pixel TFT display shows system information. The display of six tiles on the display can be configured. For example, the power at the grid connection, status information of chargers, the status of the SG-Ready interface, the value of the dynamic electricity price, etc. can be displayed. The display turns off after 5 minutes of inactivity.
Additionally, the WARP Energy Manager has a front button. Pressing this button switches between different screens. Additionally, the button color indicates whether there are problems (red color) or not (green color).
Applications
PV Excess Utilization
If a photovoltaic system is present, you want to use as much of your own produced electricity as possible. The WARP Energy Manager can help by charging electric vehicles with this electricity (PV excess charging). The electricity can also be used to operate a heat pump in extended mode, for example. Additionally, other consumers such as heating elements can be connected to the relay outputs. The Energy Manager can then switch these on, for example, when there is still PV excess left despite electric vehicle charging and heat pump control.
For PV excess utilization, the WARP Energy Manager requires an electricity meter at your grid connection to determine the excess, i.e., the feed-in of electrical power into the grid. The WARP Energy Manager then controls the devices so that no power is fed into the grid (grid consumption = 0) or a defined grid consumption is maintained. This depends on the settings. See the list of compatible electricity meters.
The key point here is that only power regulation takes place; the individual phase currents are not regulated. Since the grid operator's electricity meter, which determines electricity costs, operates in a balancing manner, phase current regulation is not necessary.
Static Load Management
When multiple chargers share a common supply line, the maximum current is often limited by this supply line. As an example, several chargers could share a 32A line. Two chargers could each be operated as 11kW chargers (2x16A). However, it would also be possible to operate one charger at 32kW (32A) if the second charger is not being used. Static load management is used for these applications.
The WARP Energy Manager can handle static load management for the chargers. No electricity meter is necessary here; only the maximum current of the supply line needs to be defined. This current must be available at all times. The energy manager distributes the current among the controlled chargers according to demand.
Dynamic Load Management
In some cases, dynamic load management at the phase current level is required. A typical example of this is rental properties where the grid connection of the property is insufficient to operate multiple chargers simultaneously. The grid connection protection limits the permissible phase current.
In the simplest case, a certain phase current can be guaranteed for all chargers. In this case, the chargers can perform static load management, where the available phase current is divided among the WARP Chargers.
However, often it cannot be guaranteed that a certain phase current is always available for charging processes, as the chargers share the grid connection with other consumers. When these consumers are switched on and off, the phase current available for the chargers changes constantly. In this case, dynamic load management is necessary to ensure that the maximum phase current is not exceeded and no fuse trips.
The WARP Energy Manager enables dynamic load management at the phase current level. This requires an electricity meter at the grid connection that can be evaluated by the energy manager. The energy manager monitors the available phase current from the grid connection and regulates the power of the chargers accordingly. This ensures that the maximum phase current is not exceeded and no fuse trips. If a photovoltaic system is present and producing energy, it automatically increases the available power for the energy manager to optimize charging of electric vehicles.
Combination PV + Load Management
PV excess utilization and static or dynamic load management can be combined. The WARP Energy Manager then operates power regulation for PV excess charging while ensuring that phase current limitations are maintained through load management.