PV Excess Charging
With photovoltaic excess charging, the goal is to charge the unused power from a photovoltaic system into an electric vehicle instead of feeding it into the power grid. Maximizing self-consumption of electricity is the priority here.
How It Works
If an appropriate energy meter is available, the charger can control the charging process to regulate to a target grid consumption.
Typically, this involves an energy meter at the grid connection (also called mains connection), which should be regulated to a consumption of 0 W. This means all PV power should be charged into the vehicle without drawing from the grid ("PV excess").
WARP3 Charger Smart and Pro are equipped with two separate contactors and can thus internally switch between single-phase and three-phase charging. Switching to single-phase charging offers the advantage that even small power surpluses can be charged into a vehicle (from approx. 1.4 kW), whereas three-phase charging enables the respective maximum power of the charger (11 kW or 22 kW).
When PV excess charging is set up, four charging modes are available:
Off: All charging processes are stopped
PV: Vehicles are only charged from PV excess. If insufficient excess is available, the charging process is stopped.
Min+PV: Vehicles are charged from PV excess. If insufficient excess is available, power is drawn from the grid so that charging processes are not stopped. The permitted grid consumption can be configured.
Fast: Vehicles are charged as fast as possible, regardless of how much PV excess is available.
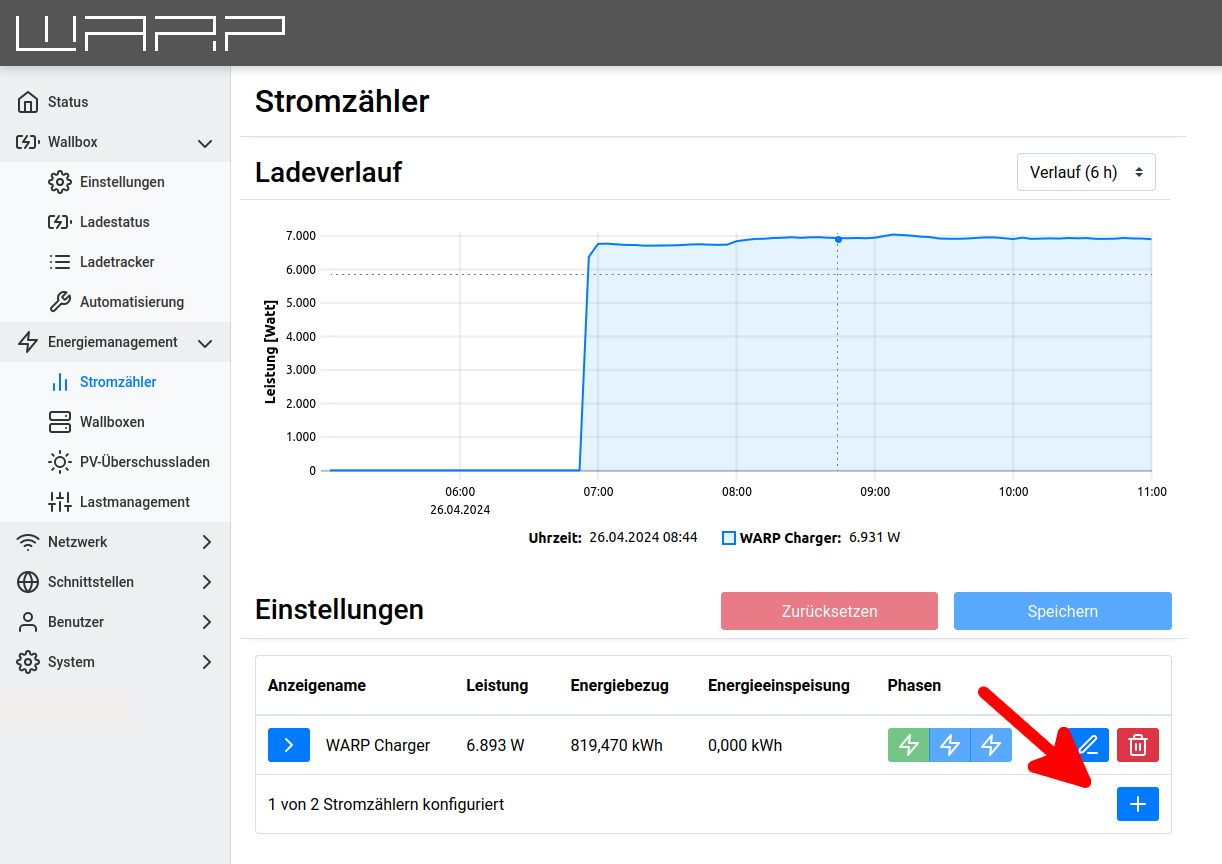
Step 1: Energy Meter Configuration
To set up PV excess charging, an energy meter must first be added that can measure the PV excess.
The energy meter is added via the Energy Management -> Energy Meters page.
There, under "Settings", a meter can be selected via the "+". For
a WARP Charger Pro, the meter in the charger is already present here and
another must be added. For a WARP Charger Smart, the meter at the grid connection
is sufficient for PV excess charging, which can measure the PV excess.
For this, the meter must supply the value "Active power (consumption minus feed-in) sum
across L1, L2, L3".
Further information is available in the web interface documentation: Energy Meters
Different meter types can be added. Devices (usually inverters) that support SunSpec are supported. Furthermore, there is support for several proprietary manufacturer protocols, including SMA and SunGrow. Another option is to create the meter virtually via the API through home automation or similar.
See List of supported and tested devices.
In the following example, we add a KOSTAL Smart Energy Meter as a meter. For this, only the IP address of the meter needs to be entered and "Start Search" clicked.
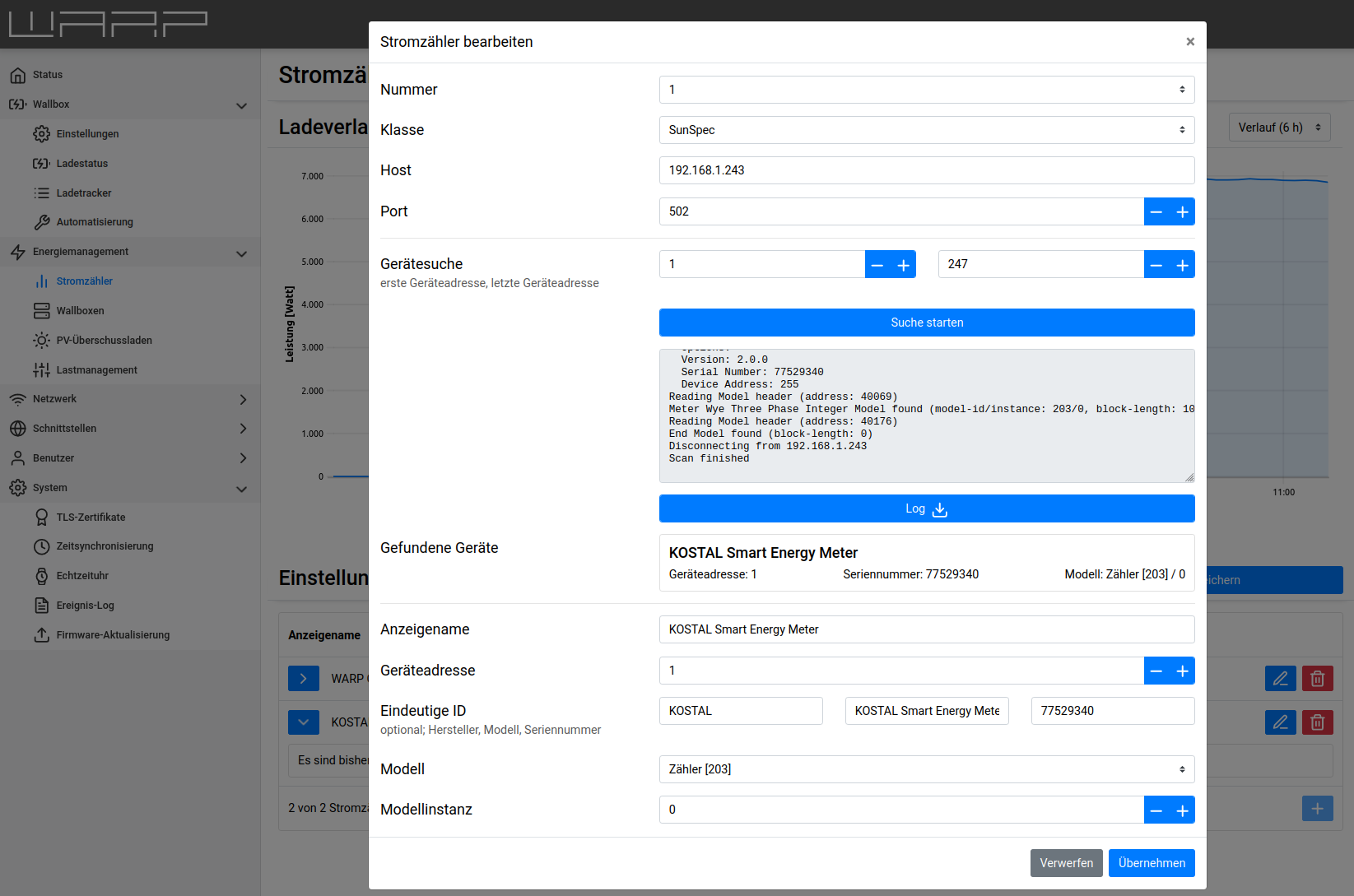
Then you must click on apply once more and then on "Save" so that the new settings are applied.
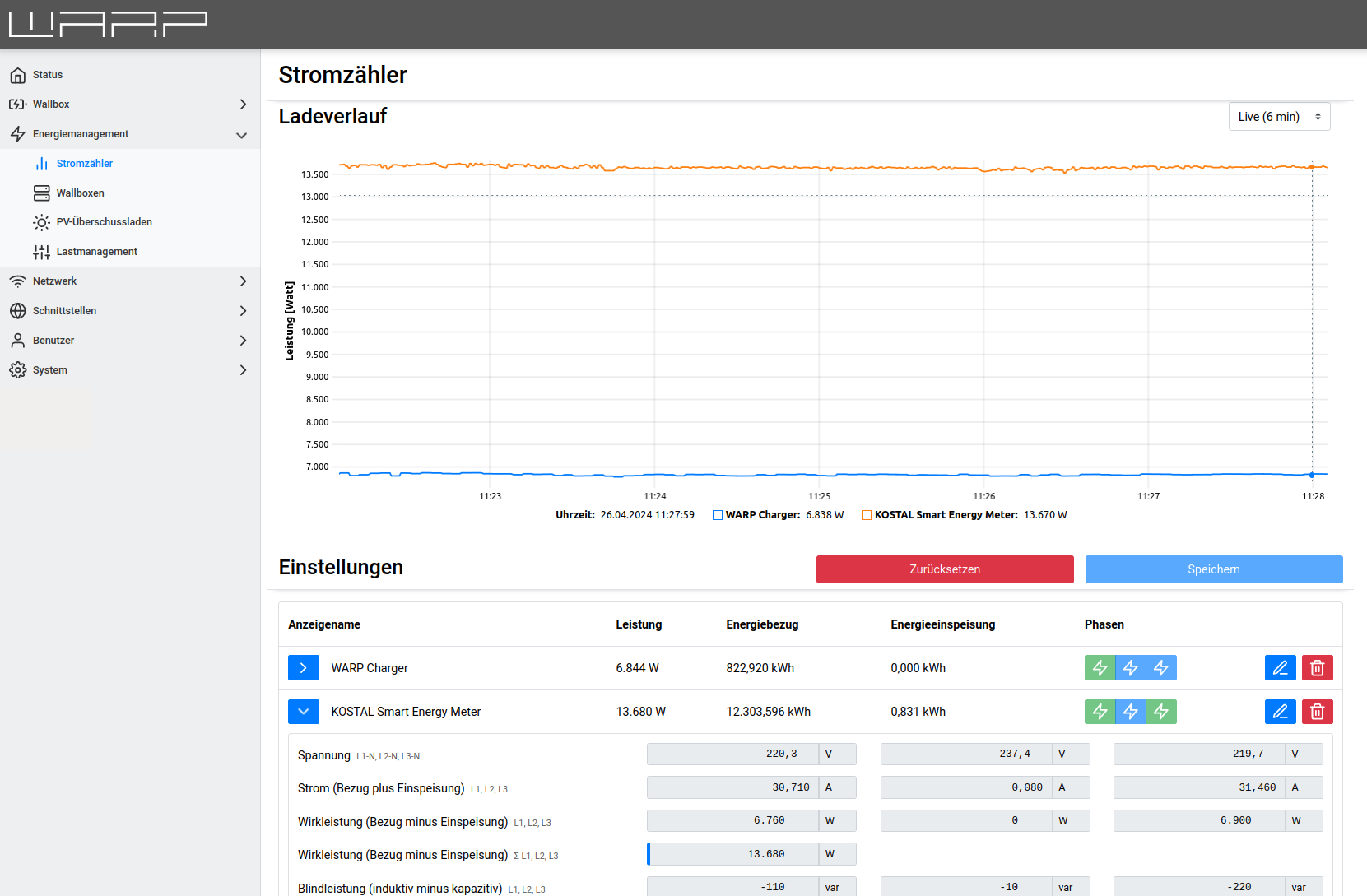
The meter then appears in the list of meters and is also displayed in the charging history.
Step 2: Excess Charging Configuration
After the meter has been added, PV excess charging can be configured under
Energy Management -> PV Excess Charging.
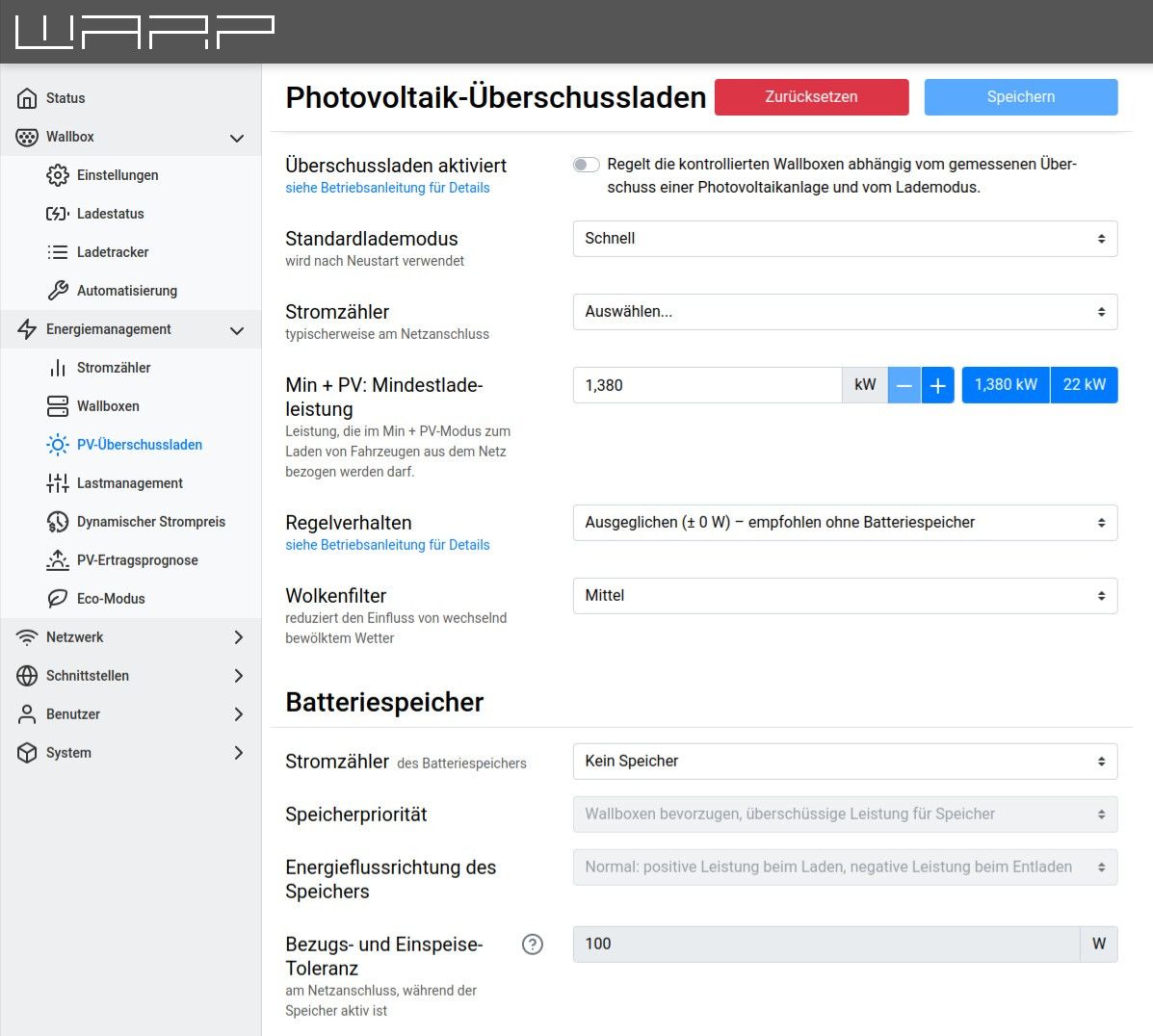
The following settings can be made:
Excess charging enabled: Switches the PV excess controller on or off.
Switching mode: Defines the behavior of phase switching.
Default charging mode: The charging mode used when the WARP3 Charger restarts.
Energy meter: The energy meter used to measure PV excess. This energy meter must be created beforehand according to the section above.
Min+PV: Minimum charging power: Defines which power may be drawn from the grid in "Min+PV" charging mode.
Control behavior: Defines to which grid consumption the control should regulate, so that for example a battery storage is prioritized higher or lower than charging vehicles.
Cloud filter: Adjusts the inertia of the control. In partly cloudy weather, it is advisable for the control to react sluggishly so that brief fluctuations in PV power are smoothed out.
Further information is available in the web interface documentation: PV Excess Charging
Battery Storage
If battery storage is present, it regulates against the PV excess control. If the battery storage can be read via an energy meter, the storage can be directly considered by the control. For this, the following settings must be made:
Energy meter: The energy meter associated with the battery storage.
Storage priority: Here you can configure whether chargers or the storage are prioritized higher.
Consumption and feed-in tolerance: The control value to which the system regulates.